HTML (HyperText Markup Language) serves as the foundation for structuring and organizing website content on the World Wide Web. It provides the essential framework, or “skeleton,” that web developers use to build modern websites and web applications.
What is HTML?
In simple terms, HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the core building block used to create and structure content on websites.
Breaking Down “HyperText Markup Language”
HyperText
HyperText refers to a method of organizing and linking text, enabling users to navigate seamlessly between different sections of the same web page or between entirely different web pages. It forms the backbone of interconnectivity on the web.
Markup Language
A markup language is a type of computer language designed to define the structure and formatting of text documents. It uses a system of tags to identify elements within a document, allowing browsers or applications to interpret and display the content in a structured and visually appealing manner.
Example of HTML
Let’s see a simple example of HTML.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Preethamrs.com</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML Tutorial</h1>
<p>You'll learn about HTML.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output :
Explanation of the HTML Structure
Here’s what each element in a basic HTML structure does:
<!DOCTYPE html>
Declares that the document is an HTML5 document. It helps browsers interpret and display the content correctly.<html>
The root element of the HTML document. It encloses all other elements in the page, marking the start and end of the HTML content.<head>
Contains metadata about the webpage, such as its title, character encoding, linked stylesheets, and other non-visible information.<title>
Specifies the title of the HTML page, displayed in the browser’s title bar or tab.<body>
The main container for the page’s visible content, including headings, paragraphs, images, links, and other elements.<h1>
Defines a level 1 heading, typically used for the main title or heading of the page. It’s the most important heading element for SEO and accessibility.<p>
Defines a paragraph of text. It’s used to structure written content on the page into readable blocks.
This structure ensures a well-organized, accessible, and functional webpage.
How Does HTML Work?
HTML works by defining the structure and content of a webpage through the use of tags. These tags serve as building blocks, describing the role and purpose of the enclosed content.
Each HTML tag has a specific function, making it easy for web browsers to interpret and render the content appropriately.
Example
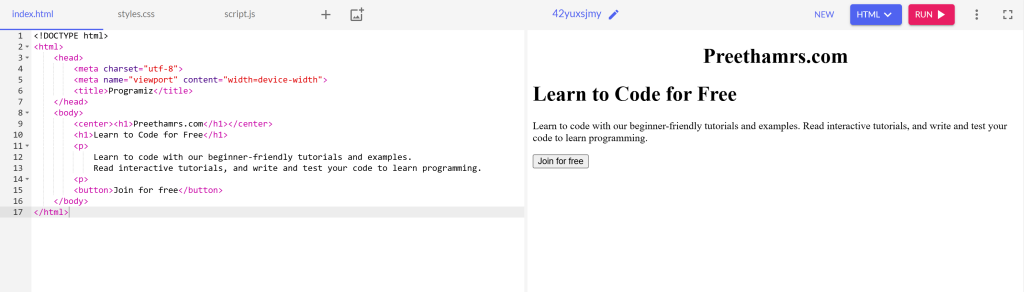
As you can see, a web browser reads HTML tags and displays them on the browser by interpreting their meaning. In the above code:
<h1>tag – displays the content inside it as a heading<p>tag – displays the content inside it as a paragraph<center>tag – displays contents inside it at the center of the page
How to create and run an HTML file?
You will need a text editor and a web browser to create and run an HTML file on your computer. You can follow the following steps to create and run an HTML file on your device.
- Open a text editor. There are many text editors available, such as Notepad (on Windows) or TextEdit (on macOS).
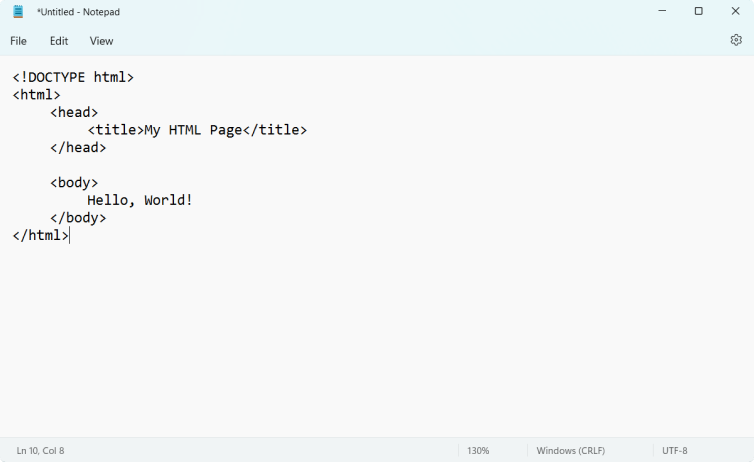
2. You can now start writing HTML code in your text editor. Here’s a sample code you can type:
3. Save the file as index.html (or any other name with the .html extension) in your desired location.
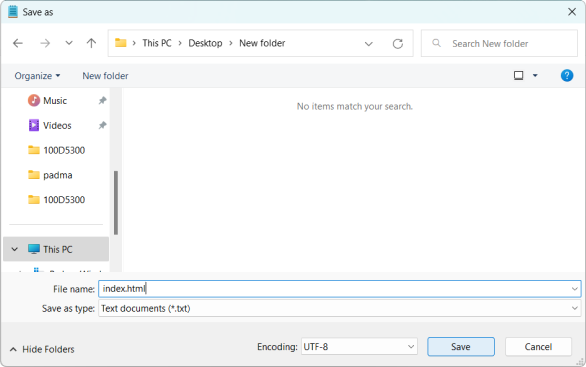
4. Open the HTML file in a web browser. You can do this by double-clicking the HTML file in the location where you saved it, or right click on your HTML file and choosing open.
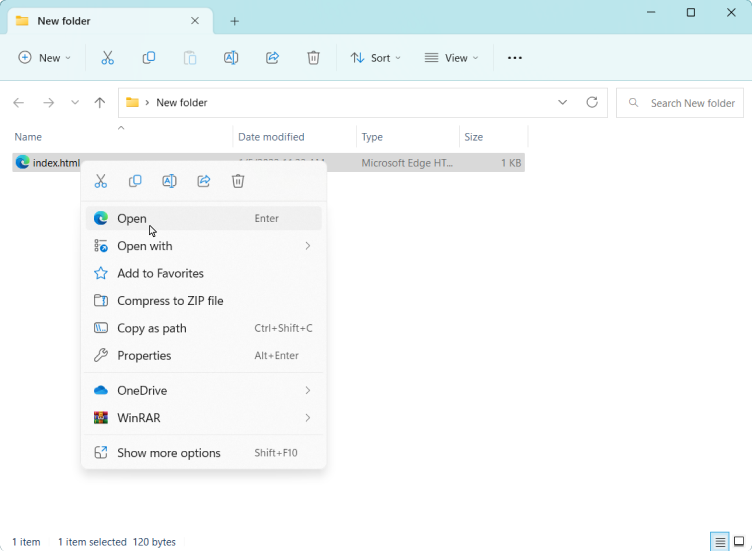
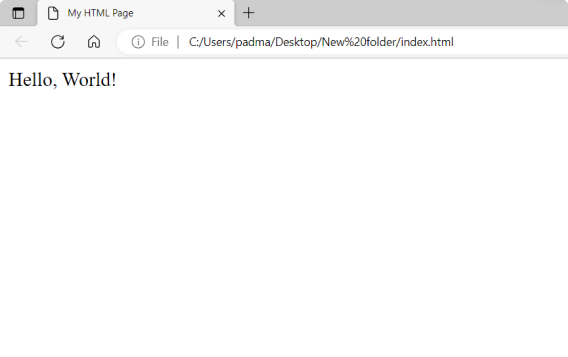
5. The HTML file will be displayed in the web browser, and you can view the content of the file.
HTML Features
HTML is a text-based language used to create web pages. It has several features that make it a powerful and widely used language for creating web pages. Some of these features include:
- HTML is a standard language used for creating and structuring web pages. It allows for the organization of content using elements such as headings, paragraphs, lists, and tables.
- It supports a wide range of media types, including text, images, audio, and video, which makes web pages more engaging and interactive.
- HTML is a flexible language that can be used with other technologies, such as CSS and JavaScript, to add additional features and functionality to a web page
- Since HTML is compatible with all browsers, web pages created in HTML are displayed across a variety of platforms and devices.
- Furthermore, it is an open and standardized language, which is constantly being updated and improved by a community of developers and experts
Cons of HTML
Here are some of the cons of using HTML:
- text-based language, which can make it difficult to read and write
- may not be powerful enough to handle some of the more complex features found in modern web pages
- can be challenging to maintain and update over time